In recent years, vegetarian diets have gained significant popularity, not just for ethical or environmental reasons but also for their potential health benefits. According to experts, a well-planned vegetarian diet can provide all the necessary nutrients, support weight loss, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. This article delves into the intricacies of vegetarianism, its nutritional benefits, and practical tips for adopting and maintaining a healthy vegetarian diet.
Understanding Vegetarianism
Vegetarianism, in its various forms, excludes meat but may include dairy products and eggs. The primary types are:
- Lacto-vegetarian: Includes dairy products but excludes eggs.
- Ovo-vegetarian: Includes eggs but excludes dairy products.
- Lacto-ovo vegetarian: Includes both dairy products and eggs.
- Vegan: Excludes all animal products, including dairy, eggs, and honey.
With growing awareness about plant-based diets, many people are considering vegetarianism for its health benefits.
Is a Vegetarian Diet Healthy?
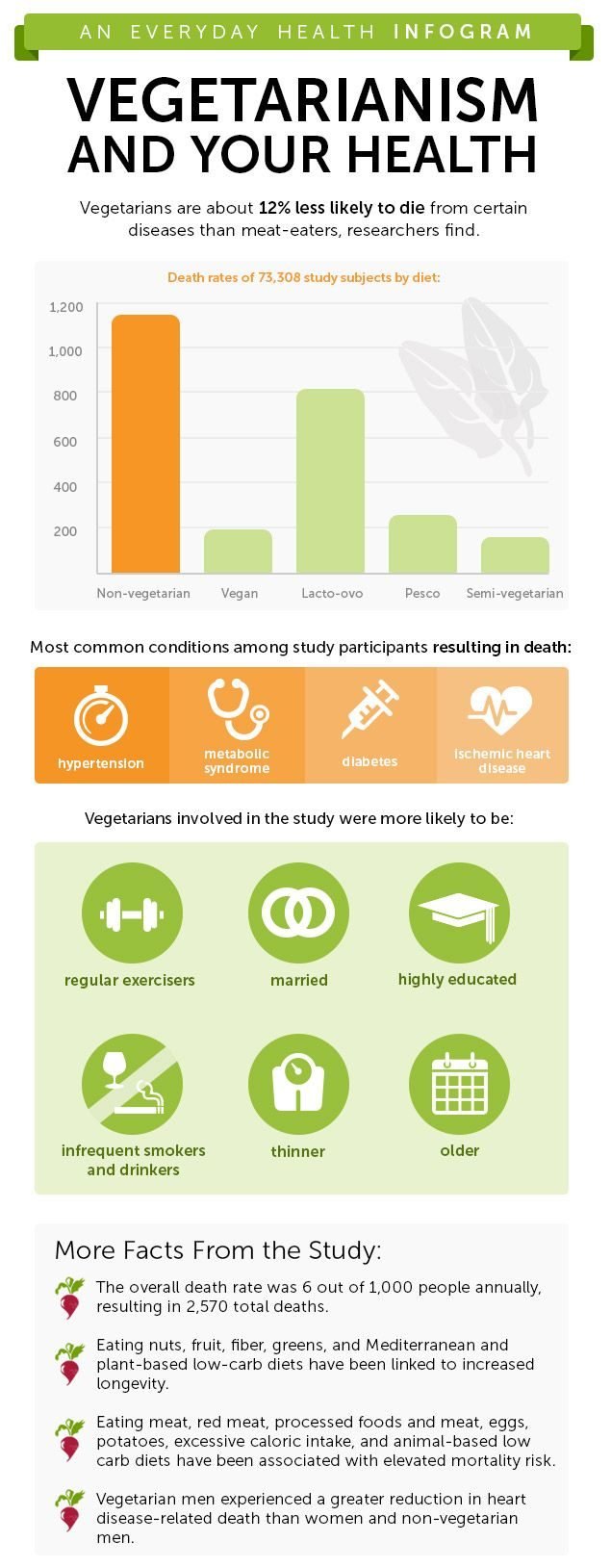
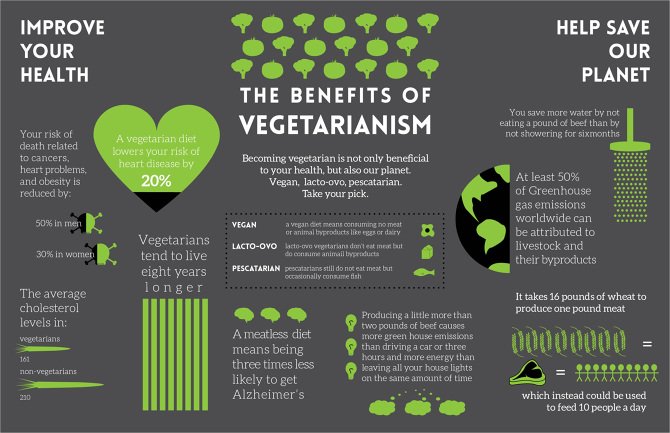
A vegetarian diet, when well-balanced, can be incredibly healthy. According to a study published in The Journal of Nutrition, vegetarians tend to have lower levels of LDL cholesterol, lower blood pressure, and reduced risks of heart disease, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes. Moreover, vegetarians often have a lower body mass index (BMI) and lower overall cancer rates.
However, it is crucial to ensure that a vegetarian diet includes all essential nutrients. Key nutrients to focus on include:
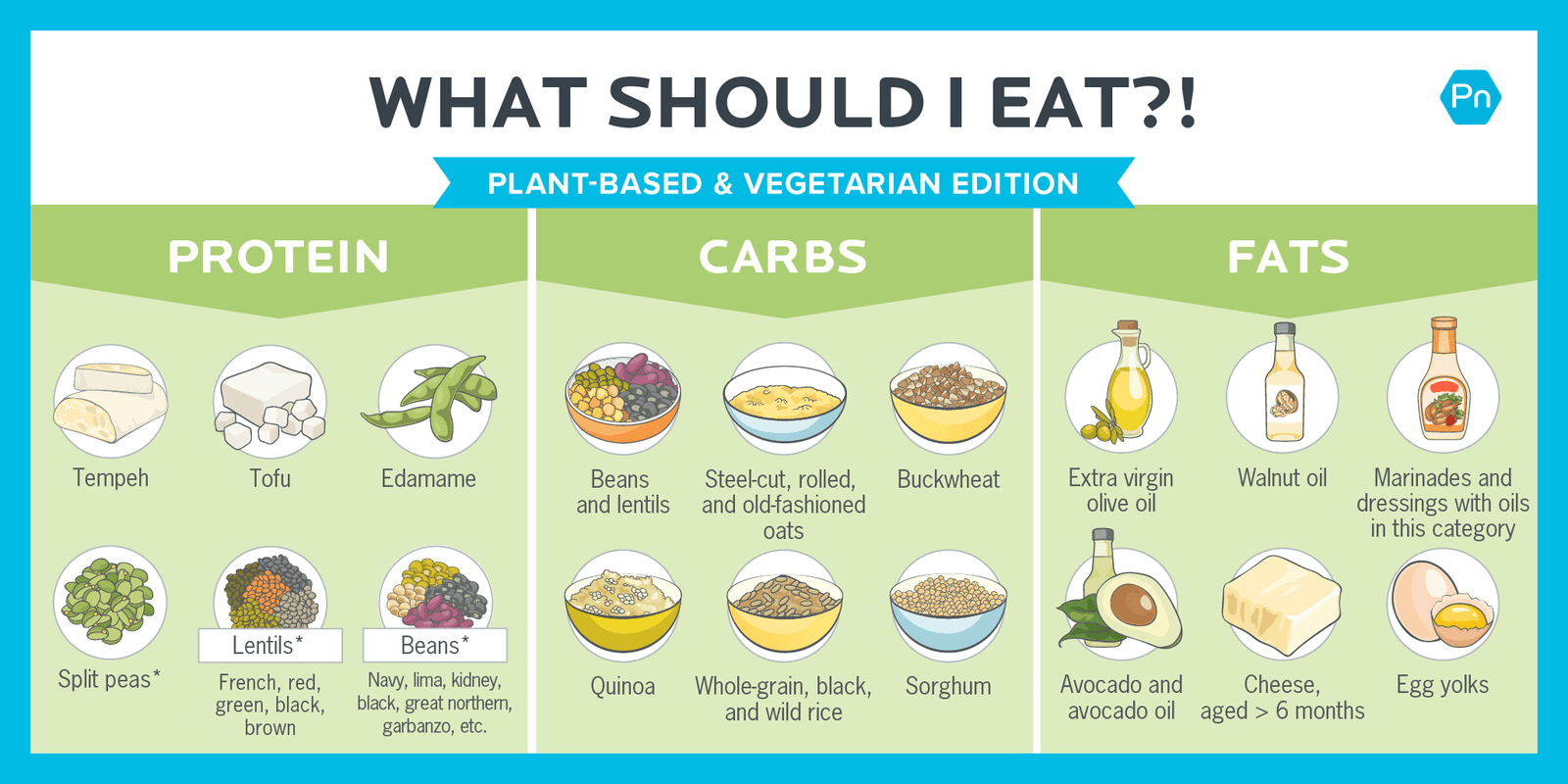
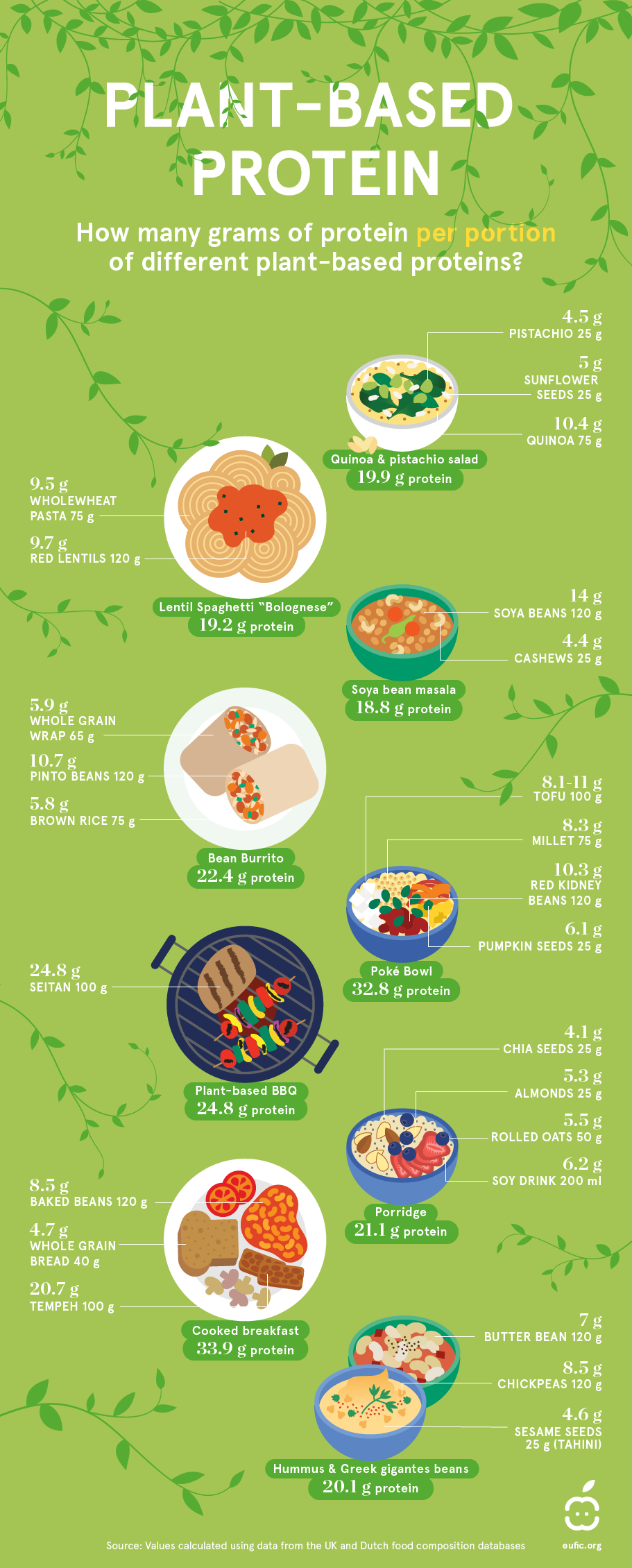
- Protein: Essential for muscle repair and growth. High protein vegetarian diet options include beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, quinoa, and seitan.
- Iron: Vital for blood production. Iron-rich vegetarian foods include spinach, lentils, chickpeas, and fortified cereals. Combining these with vitamin C-rich foods can enhance iron absorption.
- Calcium: Important for bone health. Sources include fortified plant milks, tofu, almonds, and leafy green vegetables.
- Vitamin B12: Crucial for nerve function and blood formation, often found in fortified foods and supplements.
Vegetarian vs. Vegan Diet: A Comparative Analysis
While both vegetarian and vegan diets emphasize plant-based nutrition, they differ significantly in their restrictions. Vegetarians may consume dairy and eggs, providing a broader range of nutrient sources. In contrast, a vegan diet excludes all animal products, necessitating careful planning to avoid deficiencies.
According to a study by The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, both diets can meet nutritional needs if properly planned. However, vegans need to pay extra attention to nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Tips for Starting a Vegetarian Diet

Transitioning to a vegetarian diet can be smooth with the right approach. Here are some tips on how to start a vegetarian diet:
- Educate Yourself: Understand the nutritional needs and sources of essential nutrients.
- Plan Your Meals: Incorporate a variety of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
- Gradual Transition: Start by incorporating more plant-based meals and reducing meat intake gradually.
- Experiment with Recipes: Try new vegetarian recipes to keep your meals exciting and varied.
- Consult a Nutritionist: Especially if you have specific health concerns or dietary needs.
High Protein Vegetarian Diet Plan
For those concerned about protein intake, a high protein vegetarian diet plan can be both satisfying and nutritious. Here is a sample plan:
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt with chia seeds, berries, and a drizzle of honey.
- Lunch: Quinoa salad with chickpeas, cucumbers, tomatoes, and a lemon-tahini dressing.
- Snack: A handful of almonds and an apple.
- Dinner: Lentil stew with sweet potatoes, kale, and a side of brown rice.
- Snack: A smoothie made with spinach, banana, and almond butter.
This plan ensures a balanced intake of proteins, vitamins, and minerals essential for health.
Jace’s Vegetarian Journey
Consider Jace, a vegetarian dining at a local restaurant. He opts for a grilled tofu salad with an assortment of vegetables. To make his meal healthier, Jace can request a dressing made from olive oil and lemon juice instead of a creamy, high-calorie dressing. This change reduces unhealthy fats and adds beneficial antioxidants.
Best Vegetarian Diet for Weight Loss

A vegetarian diet can be an effective strategy for weight loss. The best vegetarian diet for weight loss includes:
- High Fiber Foods: Whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and legumes that keep you full longer.
- Low-Calorie Foods: Focus on nutrient-dense but low-calorie foods like leafy greens and vegetables.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate sources like avocados, nuts, and seeds in moderation.
- Protein-Rich Foods: Include beans, lentils, tofu, and quinoa to support muscle maintenance and repair.
Plant-Based Nutrition Certification
For those looking to deepen their knowledge, obtaining a plant-based nutrition certificate can be beneficial. This certification provides comprehensive education on the benefits and implementation of plant-based diets, helping individuals make informed dietary choices.
Diabetic Vegetarian Diet
A well-planned diabetic vegetarian diet can help manage blood sugar levels effectively. Key strategies include:
- Low Glycemic Index Foods: Opt for foods that do not spike blood sugar, such as whole grains, beans, and non-starchy vegetables.
- Consistent Carbohydrate Intake: Spread carbohydrate intake throughout the day to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Healthy Fats and Proteins: Include nuts, seeds, tofu, and low-fat dairy to balance meals.
Conclusion
Incorporating a vegetarian diet can be a healthy choice, offering numerous benefits when done correctly. Whether you’re looking to lose weight, manage diabetes, or simply improve your overall health, a well-planned vegetarian diet can be your path to success. By focusing on a variety of nutrient-dense plant-based foods and being mindful of your nutritional needs, you can thrive on a vegetarian diet.
For more information on plant-based diets and nutrition, consult a registered dietitian or explore resources like the American Dietetic Association and The Vegetarian Society.
—
This article provides a comprehensive overview of vegetarian diets, backed by expert insights and scientific studies, making it a valuable resource for anyone considering this lifestyle change.
Related Infographics: