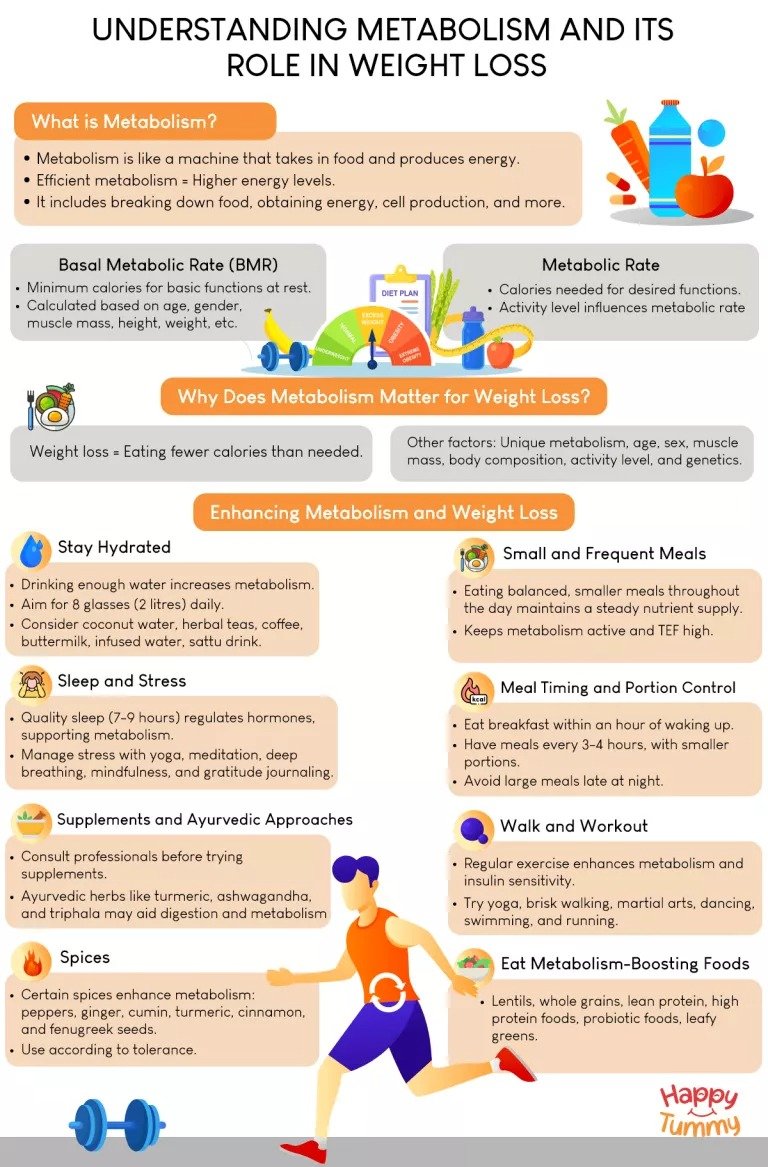
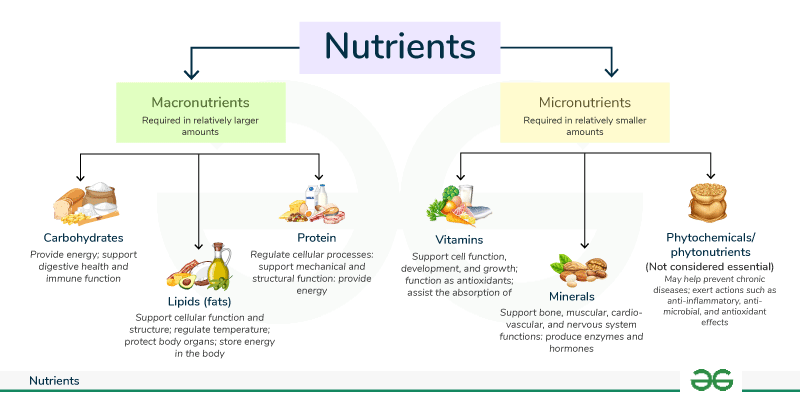
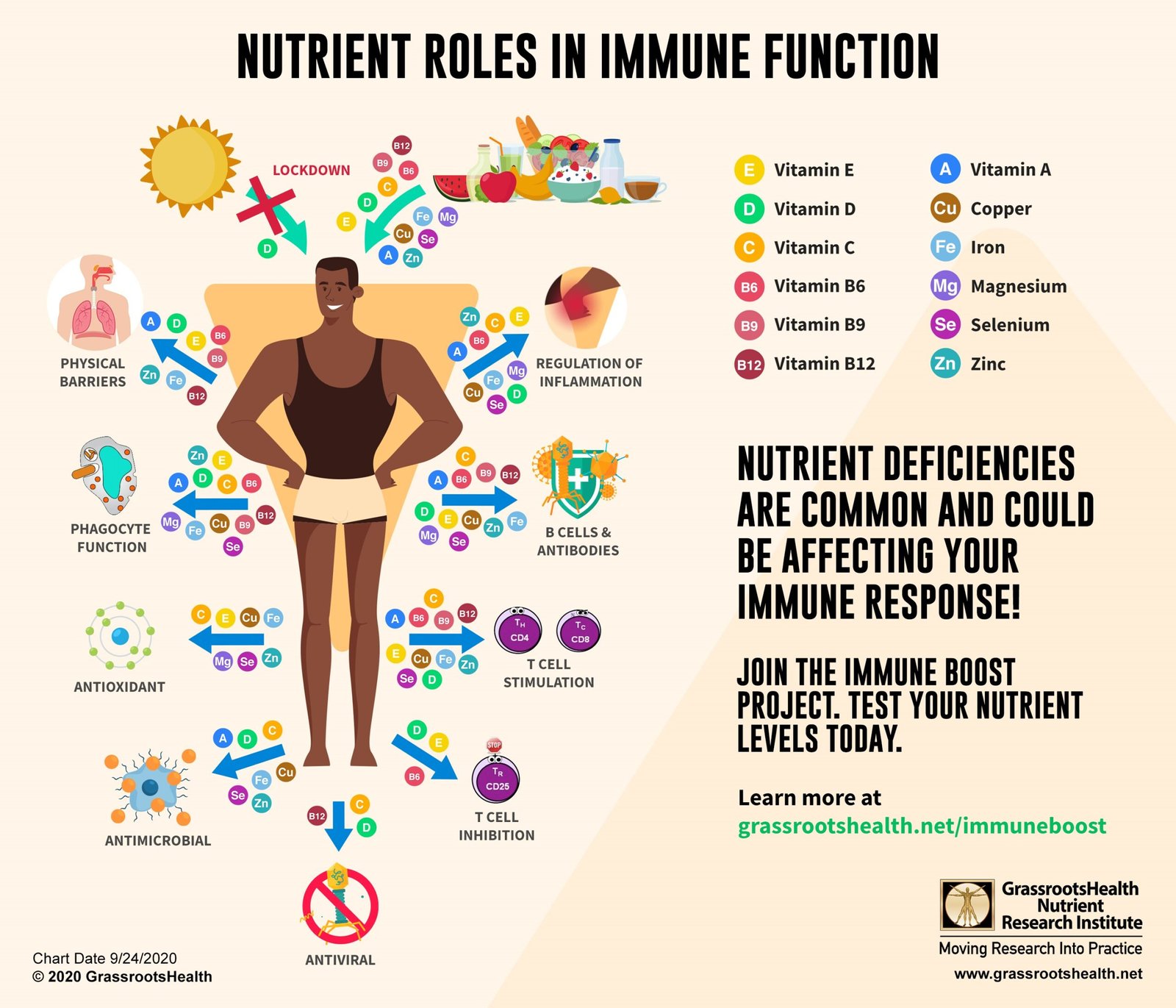
Which Nutrient is Required for Regulating Metabolism and Maintaining Normal Growth? : When it comes to maintaining a healthy body, metabolism and growth are two critical processes that work hand in hand. Both are deeply influenced by the nutrients we consume, with some being more vital than others. While Vitamin D is often spotlighted for its crucial role, there are other essential nutrients like iodine and protein that also play significant roles in regulating metabolism and maintaining normal growth.
The Power of Vitamin D: The Sunshine Vitamin
Vitamin D, often dubbed the “sunshine vitamin,” is vital for many bodily functions, including metabolism regulation and promoting healthy growth. This fat-soluble vitamin can be synthesized in the skin upon exposure to sunlight, though many people still fail to get enough, particularly those in regions with limited sun exposure.
Regulating Metabolism: The Role of Vitamin D
- Calcium Absorption: Vitamin D is essential for the absorption of calcium, a mineral critical for bone health. Without sufficient Vitamin D, calcium cannot be absorbed efficiently, leading to weakened bones and a slower metabolism.
- Insulin Sensitivity: Vitamin D improves insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for regulating blood sugar levels and metabolism. Poor insulin sensitivity can lead to metabolic disorders, including Type 2 diabetes.
- Thyroid Function: The thyroid gland, which plays a pivotal role in metabolism, relies on adequate Vitamin D levels to function properly. A deficiency can result in thyroid imbalances, slowing down metabolic processes and leading to weight gain and fatigue.
Iodine: The Metabolism Regulator
While Vitamin D plays a significant role in metabolism, iodine is another critical nutrient that often goes unnoticed. Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones, which are the main regulators of metabolism.
How Iodine Supports Metabolism and Growth
- Thyroid Hormone Production: Iodine is a key component of the thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones regulate the speed of your metabolism, influencing how quickly your body uses energy. Without sufficient iodine, thyroid hormone production decreases, leading to hypothyroidism—a condition characterized by a sluggish metabolism, weight gain, and fatigue.
- Growth and Development: Iodine is also crucial for brain development and growth, particularly during pregnancy and early childhood. A deficiency in iodine can lead to developmental delays and growth problems in children.
Sources of Iodine
To ensure adequate iodine intake, consider adding these foods to your diet:
- Seafood: Fish, seaweed, and shellfish are excellent sources of iodine.
- Dairy Products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese can also contribute to your iodine intake.
- Iodized Salt: Using iodized salt in your cooking is a simple way to ensure you’re getting enough iodine.

Protein: The Building Block of Growth
Protein is often associated with muscle building, but its role extends far beyond that. Protein is essential for growth, tissue repair, and maintaining a healthy metabolism.
Protein’s Role in Metabolism and Growth
- Muscle Growth and Repair: Protein is the building block of muscles. Adequate protein intake is necessary for muscle repair and growth, especially in children and adolescents. During growth spurts, the body requires more protein to support the development of new tissues.
- Thermogenesis: Protein has a high thermic effect, meaning it requires more energy to digest compared to fats and carbohydrates. This process, known as diet-induced thermogenesis, boosts metabolism, helping you burn more calories throughout the day.
- Satiety and Weight Management: Protein-rich foods increase satiety, helping you feel full longer. This can prevent overeating and support healthy weight management, which is essential for maintaining a balanced metabolism.
Sources of Protein
Incorporate these protein-rich foods into your diet to support metabolism and growth:
- Lean Meats: Chicken, turkey, and lean cuts of beef are excellent sources of high-quality protein.
- Fish: Fish like salmon and tuna not only provide protein but are also rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which support heart health.
- Plant-Based Sources: Beans, lentils, tofu, and quinoa are great protein options for vegetarians and vegans.
Conclusion: A Balanced Approach to Nutrient Intake
While Vitamin D, iodine, and protein are key players in regulating metabolism and supporting normal growth, they are most effective when consumed as part of a balanced diet. Each of these nutrients works synergistically with others to ensure your body functions optimally.
Ensuring adequate intake of these nutrients through a combination of sunlight, a well-rounded diet, and supplements if necessary, is crucial for overall health. Whether you’re looking to boost your metabolism, support healthy growth in children, or maintain your own health, focusing on these nutrients will help you achieve your goals.
Related Infographics: