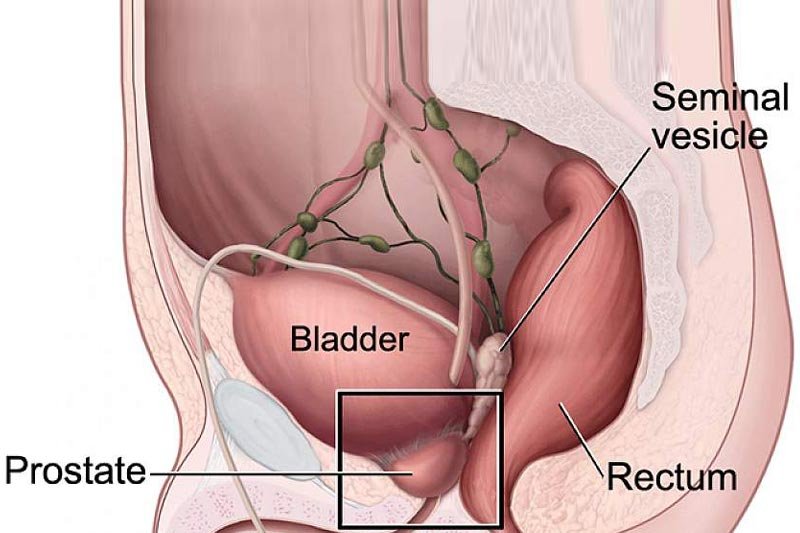
What Causes Prostate Cancer and Symptoms
Feeling the necessity to make multiple runs to the washroom? Finding it hard to urinate, or did you spot blood in that urinal? Do continue reading then, because these could be the early signs of prostate cancer that are often ignored or sidelined as a minor urinary infection.
Prostate cancer causes are determined by factors such as age, weight, race, and family history. You are at a higher risk of being affected by it as you age or if you are obese. A family history of the same or breast cancer of type BRCA1 / BRCA2 also puts you on the list of being a possible victim. Recent studies suggest that men with darker skin are more prone to be affected by aggressive prostate cancer due to reasons undetermined.
How is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed?
So, how can one diagnose to outweigh the risks? Prostate cancer can be screened by either taking a Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test or a digital rectal exam (DRE).
Usually, a man without any traces of prostate cancer will have his PSA level under 4mg/mL. On developing cancer, PSA levels will go above 4.1. Men with a PSA level in the range between 4 to 10 (borderline) have a chance of having prostate cancer. If the PSA level is more than 10, then the person has a 50% chance of being severely affected by the same.
Treatment options for Prostate Cancer
Once the patient is diagnosed, there are multiple options for treatment in the market; these options depend on factors such as the patient’s age, stage of cancer, and patient’s health.
These treatment options include:
- Bisphosphonate therapy:
When cancer spreads to a patient’s bones, this treatment is used. It includes giving drugs like zoledronate.
- Chemotherapy:
The treatment is used to stop the growth of cancer cells or to eliminate them. Chemotherapy also uses drugs and has two ways of drug supply, systemic and regional chemotherapy.
- Hormone therapy:
This includes using hormones to either block the working hormones or to remove them from the body to stop the growth of cancer cells.
- Biologic therapy:
Here, the patient’s immune system is used to fight against cancer by providing it with lab-created substances, for example, Sipuleucel-T.
- Radiation therapy:
Using radiation to eliminate and stop cancer cell growth. It has three types:- Internal
- External
- Radiopharmaceutical
- Active surveillance:
Given to older men with slow-moving cancer or when it is caught at an early stage.
Outlook & Prognosis
Prostate cancer, followed by skin cancer is the second most common of its type found in men. Statistics say that one out of seven cases of prostate cancer is seen, in men every year. However, with better research and treatment facilities, the survival rate has gone up. The survival rate depends upon the extent to which it is spread or at what stage it is diagnosed. These stages are:
- Stage 1: Cancer is localized in the prostate itself.
- Stage 2: This is an advanced stage, but the cancer is still in the prostate region.
- Stage 3: Here, cancer could have spread beyond the prostate into other distant parts of the body.
- Stage 4: Here, all the above steps are combined; cancer has spread to the other parts.
Is surgery necessary?
Due to advancements in medical science and technology, the success rate of surgery is higher than before. Prostate removal surgeries add three years to the lives of the patients when compared with monitored cases. Although surgery is the best option for all the instances of advanced prostate cancer, the early stages, and evidence of slow-moving cancer should consider other treatment options before the surgery because various tests have proven that in these cases, active surveillance may be the best management option.
Road to recovery
Even though there are a variety of treatment options, for all advanced cases, the best go is surgery. However, the operation takes a toll on the body, and even after 2-3 days of hospital recovery, the patient should follow these steps to recover fully:
- Using a Catheter: After surgery, one must maintain a catheter for at least 2-3 weeks until the urethra heals.
- Pain medication: It is necessary to take over-the-counter medications.
- Rest: An essential part of recovery is rest, avoiding heavy lifting and other strenuous activities.
- Check on side effects: Side effects like urinary incontinence or erectile dysfunction are not uncommon. So, note these side effects during the recovery time, and if they persist, check with your doctor.
- Ask your doctor: It can take about a year to recover completely from prostate surgery and communication with your doctor during this time is of utmost importance.
Related Videos about What Causes Prostate Cancer: Is it treatable?
What Causes Prostate Cancer? – The Nebraska Medical Center
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer: warning signs, diagnosis and treatment
What Causes Prostate Cancer: Is it treatable?
prostate cancer causes and risk factors, prostate cancer prevention, prostate cancer definition, causes of prostate cancer wikipedia, what is prostate cancer, prostate cancer treatment, prostate cancer diagnosis, understanding prostate cancer,